Чем прошить мицубиси аутлендер
Начал тут встречать записи в БЖ, что достаточно поставить "чудо-кнопку" и заработает ECO- режим. Это- не так. Кроме установки крышечки на кнопку нужно сделать чиповку. Это совсем не то, что тут называют "активацией". Это- полноценное обновление прошивки. "Активация"- дает только отображение листочка и шкалы, но сам режим НЕ будет работать, от слова совсем (сколько бы баков бензина вам не советовали бы сжечь- это ложь! Вы никогда не почувствуете и не увидите реакции на включение ECO-режима без чиповки, т.е. перепрошивки.
Вот именно поэтому размещаю здесь свой отзыв, написанный 10 июня 2015г, через неделю после прошивки с ECO- режимом.
Немного длинный пост получился, но он содержит сравнительный отзыв на 2 прошивки: от Ёжика и от Андрея .
Итак.
После покупки машины и поняв, что 1,6 на Форде это- самолет, по сравнению с Оутом 2,0, я начал искать возможность сделать чиповку. На моё счастье у Ёжика была запланирована поездка в Воронеж и там он мне всё сделал.
По началу нравилось- пропала тупизна и всё такое… Но со временем недостатки прошивки начали реально напрягать и я практически уже мечтал от неё избавиться. Во-первых расход выше. Что бы тут ни говорил- расход выше. Я прошивался в Воронеже, а это 120км. Поэтому на обратном пути сразу стало заметно, что расход вырос почти на литр. По городу- итого выше. Редко когда видел на приборке 14,7л. В основном- не менее 15л.
Хотя машина реально рвала с места. И это, кстати, тоже напрягало. На светофоре даже было некомфортно- приходилось давить на тормоз. Частенько переходил на N, чтобы не держать машину тормозом. Ну парковаться тоже не нравилось- чуть отпустишь тормоз- рывок. Кто-то скажет- фигня, всё нормально, мелочи. Но из мелочей всё складывается. Далее- мотор работал жёстко, с каким-то странным звуком. Я до этого не имел ММС-ных моторов и думал- "фича такая". Ну про вибрации вы все знаете- трясучка меня достала на холостых. На N и Р было не так заметно, поэтому грешил на вариатор. Как выяснилось позже- напрасно. Короче, не нравилась работа мотора и всё тут- трясучка и шум… Да, и главное- зависание оборотов на 1500 перед светофором. Т.е. едем 60км/ч, начинаем тормозить, а обороты висят на 1500 вплоть до 20км/ч. А потом резко- падают на ХХ. Тоже фигня все тут говорят. Но при торможении мотор гудит так, как ему положено гудеть при 1500 оборотов. А мы, напомню, тормозим и скорость снижается, а мотор гудит себе в одной тональности и о том, что мы тормозим- он ни сном, ни духом… Как говорится- теряется следственно-причинная связь…
В общем, все эти "фичи" чиповки меня реально достали и начали перевешивать бодрый разгон на низах. Каждый день с надеждой проверял- не собирается ли к нам Дима? Но увы…
И ТУТ СЛУЧАЕТСЯ ЧУДО!
На нашем любимом форуме появляется эта тема, созданная ув. kidanov. Олег в переписке мне сообщил, что скоро ув. andrej12 тоже сможет помочь мне в осуществлении моей мечты (в избавлении от чиповки). И вот день настал- я стал счастливым обладателем отличной прошивки с дополнительным режимом.
Т.к. всё случилось спонтанно- Андрей мне сообщил о приезде неожиданно, то вместо кнопки я по-быстрому вывел пару проводов- чисто для проверки. Но это, собственно неважно. Главное- прошивка. Как говорится первое впечатление- самое правильное, поэтому опишу после нескольких дней пользования, что из себя представляет прошивка- имхо.
После прошивки я забыл замкнуть контакты и поехал от Андрея без режима ЭКО. На стоковой прошивке. При трогании- первая мысль была- "потерял 10%". Потом понял- это не 10% потерял, а прошёл надоевший мне толчок (маленький рывок) при отпускании педали тормоза. Теперь машина разгоняется резко и без ненужного первоначального рывка. Тяга на низах точно такая же как и на Ёжиковой прошике- ничего не поменялось. Я сейчас езжу по городу- обороты не превышают 2200. Тупость коробки отсутствует (собственно- это то, ради чего мы все к Ёжику и ездили). Т.е. нажал на газ- машина едет. Ровно как на механике. Ещё Ёжикова прошивка убирает влияние кондиционера. Это- действительно так- обороты стояли на ХХ как вкопанные и на кондей не реагировали. Сейчас- есть небольшое телепание. Но это- реально телепание, т.е. чуть заметное отклонение стрелки, а не как раньше на стоке- подскакивали до 1000 и потом падали до ХХ. Этого нет, поэтому можно сказать, что проблема с этим (влиянием кондея) также в ЭКО-прошивке решена. Ну на тягу кондей ни в одной прошивке не влиял, поэтому опустим этот момент.
Далее- расход. Расход упал на 1,5-2л. Т.е. сейчас я езжу по городу и на приборке вижу 13-13,3. Это, кстати, БЕЗ включения режима ЭКО!
Т.е. напомню итог- резвость есть, задумчивости вариатора нет, Ёжиковой чиповки тоже нет, а экономия- есть. Т.о. расход даже меньше, чем был у меня на первой стоковой прошивке, не говоря о прожорливой чиповке.
По трассе стал расход около 8 л (а после Ёжиковой чиповки у меня было минимум 9,8, а до чиповки- 8,9).
Теперь про режим ЭКО. При нажатии кнопочки- на приборке загорается надпись с листочком и машина становится… тупая. Объясню как это выглядит. Начинаем трогаться как обычно (мы же привыкли к своей машине и знаем сколько надо давить на газ- это в подсознании). Так вот давим как обычно, а машина "не едет". Дело в том, что переключение скоростей происходит при 1750 оборотах. Попробуйте поездить так и поймете каково это. Т.е. режим езды пенсионерский. Но тут есть два нюанса- ездить в городе по пробкам- большего и не нужное. Самое то, что надо. Зачем жечь бензин, если всё-равно еле тащимся? И второе- если нам надо ускориться- резко давим на газ и едем как нам надо- резко и быстро. Поэтому- это идеальный вариант для города. Даже без вариантов. У меня- расход меньше на 0,5, но это из-за того, что он у меня и так почти на 2 литра до этого упал.
Поэтому те, кто прошьётся после стока получит экономию бензина в режиме ЭКО и тягу на низах в обычном режиме и исчезнет тупость вариатора.
И, что немаловажно, по слухам, эта прошивка- заводская. Да я это сразу почувствовал- мотор стал работать по-другому- тише и мягче. Зависание оборотов на 1500 перед светофорами теперь отсутствует. Теперь всё четко- тормозим- обороты падают, машина останавливается. Теперь наслаждаюсь тишиной. Накат имеется, торможения двигателем почти нет (ну это как Ёжиковой прошивке).
Самое главное (для меня)- подъехав к работе на следующий день после прошивке я с ужасом обнаружил, что на ХХ нет вибрации. Т.е. вибрация у меня была=0! (по прошествии времени могу отметить, что вибрация не ушла полностью- то есть, то нет), но вот теперь есть промежутки, когда её нет вообще.
Итог. Сказать, что я доволен- это ничего не сказать. Я- реально тащусь от езды!
п.с. andrej12, kidanov, СПАСИБО, вам, за такой отличный подарок! Молодцы ребята! Удачи, вам, во всех делах!
Дополнение 2.
(После написания отзыва начали звонить и слать в личку вопросы, пришлось продолжить эксперименты :)).
Проехал по окружной для эксперимента по обгонам.
Хотя она и загружена оказалась, но кое-что выяснил.
Так вот, про обгоны. При небольшом нажатии на газ (т.е. попытка ускорения при обгоне)- обороты резко прыгают на 3000-3500. Т.е. это, типа как, кик-даун или спорт-режим или как там это называется? Даже удивительно- т.е. чуть резче нажал- обороты прыгают на 3 тыщи и там висят. Машина естественно резко ускоряется. Но вот при переходе этих 3000 тыщ есть небольшой затуп. Скорость ускорения немного уменьшается. Тут надо дальше давить на газ, чтобы обороты быстрее перевалили этот рубеж.
Кстати, этот эффект имеется и не на трассе. Т.е. едем по городу 60км/ч, чуть резче, чем обычно нажимаем на газ- обороты прыгают на 3000. Х.з., что происходит- может пониженная включается, может просто обороты возрастают. Но это дает прибавку в мощности для осуществления обгона. После обгона бросаем газ и обороты возвращаются к нормальное состояние.
Немного странно- т.к. я раньше с такой функцией не сталкивался, но дело привычки я думаю. Тем более- это очень хорошая штуковина для резких ускорений.
Теперь вот сижу репу чешу- надо ли мне после этого делать Ds или я его уже получил на программном уровне? (в итоге оказалось Ds гораздо веселее работает— :))
На фотке виден расход.
Пока не израсходовал последнюю заправку (потратил только 13л из 47), но результат уже очевиден:

Любители активной езды рано или поздно задумываются о повышении мощности двигателя своего автомобиля. Имеет ли смысл чип тюнинг Митсубиси Аутлендер 3, можно ли произвести его самостоятельно, и если да, то что для этого потребуется.
Существует два пути возможного решения проблемы:
- внесение конструктивных изменений путём замены и доводки некоторых деталей силового агрегата;
- перенастройка программного обеспечения ЭБУ двигателя, иначе говоря – чип-тюнинг.
4B11 главный претендент на повышение мощности
Реализуемая в настоящий момент модель популярного японского кроссовера комплектуется несколькими вариантами двигателей. Наибольший интерес, с точки зрения увеличения мощности, представляет бензиновый силовой агрегат с рабочим объёмом 2,0 литра, выпускаемый в двух незначительно отличающихся версиях – 4B11 и 4J11. Дело в том, что изначально расчетная мощность этого атмосферного мотора составляла 162 л. с, но в угоду экологическим требованиям и для снижения категории налогообложения его характеристики были ограничены программно. В России у официальных дилеров можно встретить машины с паспортной мощностью 118, 146 и 150 л. с.

Чип Аутлендер 3 лучше проводить на бензиновом 4B11 2.0
Очевидно, что снятие программных ограничений не нанесёт вред конструкции двигателя. Но поскольку силовой агрегат кроссовера работает в паре с бесступенчатым вариатором, то на Мицубиси Аутлендер чип тюнинг мотора следует производить одновременно с изменением настроек CVT. В противном случае ездить на машине станет не слишком комфортно, а ресурс CVT существенно снизится.
Не стоит надеяться получить прирост мощности свыше 162 л. с. исключительно за счёт изменения настроек ЭБУ. Для серьёзного улучшения характеристик атмосферных двигателей требуется вмешательство в их механическую часть. Многие решаются на установку турбонаддува, полагая, что 4B11 конструктивно схож с T-GDI. На самом деле эти агрегаты имеют существенные отличия, среди которых другая поршневая группа и иная система впрыска. Возможностей штатной тормозной системы и вариатора кроссовера, для того чтобы контролировать возросшую мощь, окажется недостаточно.
Сомнительные кандидатуры
Выполнять чип тюнинг Мицубиси Аутлендер, оснащённого атмосферными бензиновыми двигателями большего объёма — 2,4 и 3,0 литра, не внося изменений в конструкцию силовых агрегатов, не имеет большого смысла. Ощутимо увеличить отдачу этих моторов удастся, только установив распределительные валы с изменённым профилем кулачков и прямоточную систему выхлопа.
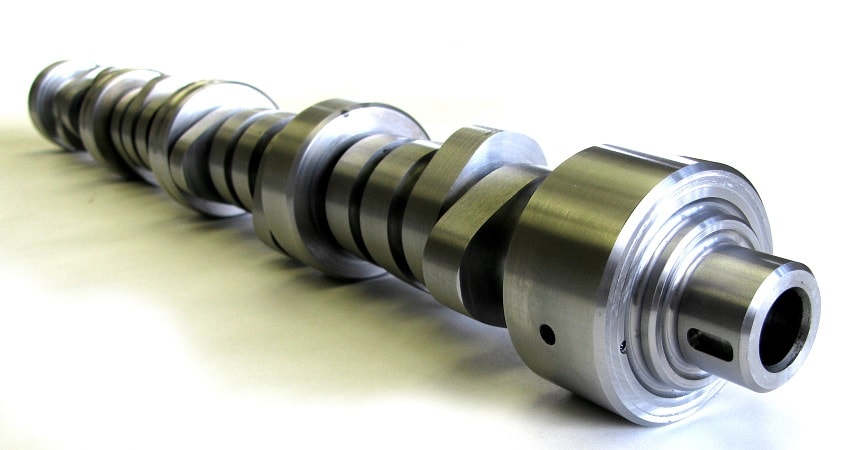

Распредвал с изменённым профилем кулачков ощутимо увеличит отдачу моторов
Корректировка программного обеспечения дизельного силового агрегата с рабочим объёмом 2,3 литра способна принести дополнительные 20 л. с. без серьёзного ущерба для конструкции мотора, общий ресурс которого всё же несколько снизится. Более значительное изменение параметров нежелательно, так как может оказаться для двигателя фатальным. С учётом хороших тяговых характеристик дизеля ценность в такой прибавке мощности остаётся под вопросом.
Обязательная подготовка автомобиля перед чиповкой
Прежде чем приступать к перепрограммированию ЭБУ, обязательно следует убедиться, что машина полностью исправна. Это касается как механической части, так и электронных компонентов. Неисправные датчики или гидрокомпенсаторы, окислившиеся контакты проводов или изношенные детали привода ГРМ сделают работу напрасной. Поэтому имеет смысл выполнять чип-тюнинг на новом, только что приобретённом автомобиле. На подержанной технике придётся начинать с проведения полной диагностики и устранения обнаруженных неисправностей.
Услуги по повышению мощности автомобильных двигателей путём перепрошивки программного обеспечения предлагают многие конторы. Цены на услуги зависят от совершенства оборудования, квалификации выполняющих работу специалистов и жадности владельцев компании. Но, в большинстве случаев, визит в мастерскую обходится дешевле, чем покупка оборудования, необходимого для того, чтобы выполнить чип тюнинг Мицубиси Аутлендер своими руками.
Необходимое оборудование и оснащение
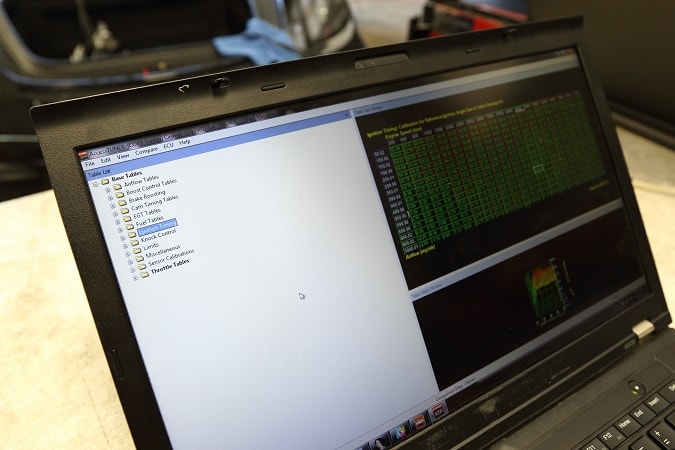
Если вы твёрдо вознамерились выполнить работу самостоятельно, придётся озаботиться приобретением необходимого оборудования и программного обеспечения. Потребуется следующее.
- Ноутбук или персональный компьютер с комплектом длинных проводов.
- Программатор. Это устройство, дающее возможность изменять программное обеспечение ЭБУ. Некоторые пытаются изготовить самостоятельно, но, во-первых, для этого необходимо обладать серьёзными профессиональными навыками, а во-вторых, малейшая ошибка в устройстве программатора может стать причиной выхода из строя электронных компонентов автомобиля. Так что, лучше не экспериментировать, а купить уже готовый прибор. В предлагаемых на рынке моделях нет недостатка, а перечислять производителей оборудования не имеет особого смысла, поскольку постоянно появляются новые игроки. Но, в качестве примера, можно упомянуть такие бренды, как K-TAG или KESS. Стоимость серьёзного оборудования колеблется в пределах 100 – 250 USD. Но можно обойтись и чем-нибудь попроще. Изделия фирм MASTER или Galetto стоят порядка 40 – 60 USD и неплохо справляются со своей задачей. При покупке программатора важно ознакомиться с его документацией и убедиться, что прибор способен выполнить чип тюнинг Аутлендер.
- Необходимое для перепрошивки ЭБУ программное обеспечение. Профессионалы предпочитают софт, вроде ChipTuningPRO, позволяющий вносить изменения в программу самостоятельно и даже разблокировать закрытые для вмешательства процессы. Но любые ошибки чреваты тем, что блоку управления потребуется замена. Не имея необходимых знаний и опыта, лучше воспользоваться софтом, вносящим корректировки в автоматическом режиме и действовать в соответствии с прилагаемой к нему инструкцией.
- Набор переходников, позволяющих подключить оборудование к соответствующему разъёму вашего автомобиля.
Перед началом работ следует точно определить производителя, модель и модификацию установленного на автомобиле ЭБУ. Ошибка даже в одной букве или цифре маркировки устройства может вам дорого обойтись.
Приобретя оборудование для диагностики и корректировки программного обеспечения, вы сможете производить чип-тюнинг различных моделей двигателей. Нужно только набраться опыта и действовать крайне аккуратно, не увеличивая мощность выше разумных пределов.
OUT III: Делаем S-AWC на Outlander: репрограмминг блока AWC. Блок S-AWC от Mitsubishi Eclipse Cross на Mitsubishi Outlander
Блок S-AWC от Eclipse Cross на Outlander
Продолжаем доработку Аута, а именно хотел поделиться своими наблюдениями об установленном блоке
S-AWC (Super All Wheell Control), как на Eclipse Cross. В целом показалось что руль стал более острей, двигатель не тупит при проезде «лежачих полицейских». Экстремально в повороты входить не пробовал пока, но говорят теперь можно! Да в режиме AUTO теперь машина едет увереннее. теперь это режим SNOW
Так, что «новомодная коробка S-AWC» пока радует. Наблюдать за ее работай буду и дальше!
Новая кнопка переключения режимов полного привода
А, вот и сама коробка S-AWC
Информация для общего развития
Режимы теперь называются иначе
Учу поиску. Дорого. С гарантией! ==>>> Подробнее тут
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Eclipse Cross==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi ASX, Peugeot 4008, Citroen C4 Aircross==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander XL, Peugeot 4007, Citroen C-Crosser==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander III (2013-2015MY)==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander IV (2015-2019MY)==>>>
Учу поиску. Дорого. С гарантией! ==>>> Подробнее тут
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Eclipse Cross==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi ASX, Peugeot 4008, Citroen C4 Aircross==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander XL, Peugeot 4007, Citroen C-Crosser==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander III (2013-2015MY)==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander IV (2015-2019MY)==>>>
Система Mitsubishi S-AWC: от концепта в реальность. Немного о эволюции системы
S-AWC (Super All Wheel Control) is the brand name of an advanced full-time four-wheel drive system developed by Mitsubishi Motors. The technology, specifically developed for the new 2007 Lancer Evolution, the 2010 Outlander (if equipped), the 2014 Outlander (if equipped), the Outlander PHEV and the Eclipse Cross have an advanced version of Mitsubishi Motors' AWC system. Mitsubishi Motors first exhibited S-AWC integration control technology in the Concept-X model at the 39th Tokyo Motor Show in 2005.[4] According to Mitsubishi Motors, "the ultimate embodiment of the company's AWC philosophy is the S-AWC system, a 4WD-based integrated vehicle dynamics control system".
It integrates management of its Active Center Differential (ACD), Active Yaw Control (AYC), Active Stability Control (ASC), and Sports ABS components, while adding braking force control to Mitsubishi Motors' own AYC system, allowing regulation of torque and braking force at each wheel. S-AWC employs yaw rate feedback control, a direct yaw moment control technology that affects left-right torque vectoring (this technology forms the core of S-AWC system) and controls cornering maneuvers as desired during acceleration, steady state driving, and deceleration. Mitsubishi Motors claims the result is elevated drive power, cornering performance, and vehicle stability regardless of driving conditions.
Components
Active Center Differential (ACD)
Active Center Differential incorporates an electronically-controlled hydraulic multi-plate clutch. The system optimizes clutch cover clamp load for different driving conditions, regulating the differential limiting action between free and locked states to optimize front/rear wheel torque split and thereby producing the best balance between traction and steering response.
Active Yaw Control (AYC)
Active Yaw Control uses a torque transfer mechanism in the rear differential to control rear wheel torque differential for different driving conditions and so limit the yaw moment that acts on the vehicle body and enhance cornering performance. AYC also acts like a limited slip differential by suppressing rear wheel slip to improve traction. In its latest form, AYC now features yaw rate feedback control using a yaw rate sensor and also gains braking force control. Accurately determining the cornering dynamics on a realtime basis, the system operates to control vehicle behavior through corners and realize vehicle behavior that more closely mirrors driver intent.
Active Stability Control (ASC)
Active Stability Control stabilizes vehicle attitude while maintaining optimum traction by regulating engine power and the braking force at each wheel. Taking a step beyond the previous generation Lancer Evolution, the fitting of a brake pressure sensor at each wheel allows more precise and positive control of braking force. ASC improves traction under acceleration by preventing the driving wheels from spinning on slippery surfaces. It also elevates vehicle stability by suppressing skidding in an emergency evasive maneuver or the result of other sudden steering inputs.
Sport ABS
The Sports ABS system supports braking when entering into a corner by controlling power to all tyres depending on handling characteristics. Braking can be controlled to obtain optimal damping at each tyre based on information from four wheel-speed sensors and steering wheel angle sensor. The addition of yaw rate sensors and brake pressure sensors to the Sport ABS system has improved braking performance through corners compared to the Lancer Evolution IX.
Concept components for 2007 Lancer Evolution
The prototype system also featured two additional components controlling suspensions and steering, which failed to make the production version of S-AWC system:
- Active Steering System
- Roll Control Suspension (RCS)
Active Steering System realizes handling with more linear response by adaptively controlling front wheel turn angle according to steering input and vehicle speed. At slower vehicle speeds the system improves response by shifting to a quicker steering gear ratio, while at higher speeds it substantially improves stability by moving to a slower gear ratio. For rapid steering inputs, S-AWC momentarily increases front wheel turn angle and Super AYC control to realize sharper response. In countersteer situations, S-AWC increases responsiveness further to assist the driver with steering precision.
RCS effectively reduces body roll and pitching by hydraulically connecting all the shock absorbers together and regulating their damping pressures as necessary. Able to control both roll and pitching stiffness separately, RCS can operate in a variety of ways. It can, for example, reduce roll only when required during turn in or in other situations while being set up on the soft side to prioritize tire contact and ride comfort. Since the system controls roll stiffness hydraulically, it eliminates the need for stabilizer bars. In the integrated control of its component systems, S-AWC employs information from RCS's hydraulic system to estimate the tire load at each wheel.
Control system
The use of engine torque and brake pressure information in the regulation of the ACD and AYC components allows the S-AWC system to determine more quickly whether the vehicle is accelerating or decelerating. S-AWC also employs yaw rate feedback for the first time. The system helps the driver follow his chosen line more closely by comparing how the car is running, as determined from data from the yaw rate sensors, and how the driver wants it to behave, as determined from steering inputs, and operates accordingly to correct any divergence. The addition of braking force regulation to AYC's main role of transferring torque between the right and left wheels allows S-AWC to exert more control over vehicle behavior in on-the-limit driving situations. Increasing braking force on the inside wheel during understeer and on the outer wheel during oversteer situations, AYC's new braking force control feature works in conjunction with torque transfer regulation to realize higher levels of cornering performance and vehicle stability.
- Tarmac for dry, paved surfaces;
- Gravel for wet or unmade surfaces;
- Snow for snow-covered surfaces.
ECU integration
Two electronic control units (ECU) regulate vehicle motion. One is an ECU developed by Mitsubishi Electric to control ACD and AYC. The other is an ECU developed by Continental Automotive Systems of Germany that controls ASC and ABS. The two ECUs can communicate with other ECUs through a CAN, an in-vehicle LAN interface standard. In addition, the two ECUs are communicating with each other through a dedicated CAN, enabling vehicle motion to be controlled more quickly. The cable and communication standard for the dedicated CAN are the same as those for other CANs.
A longitudinal acceleration sensor, lateral acceleration sensor and yaw rate sensor are installed as one module near the gravity center of a vehicle, which is located between the driver's and passenger's seats. Other sensors, such as a wheel-speed sensor and steering-angle sensor, are installed in different places. However, no vertical acceleration sensor is used.
Also, when the vehicle is equipped with Mitsubishi's Twin Clutch SST transmission, S-AWC analyzes the behavior of the turning vehicle and if it judges that it is safer not to shift gears, it sends a signal to tell Twin Clutch SST that the gear must not be changed. However, S-AWC does not control vehicle motion by using control information from Twin Clutch SST. The co-operation is a one-way communication.
The control algorithms of vehicle motion were developed by Mitsubishi in-house, with MATLAB and Simulink: control system modeling tools. Mitsubishi adopted model-based method, which combines an algorithm and physical model of a vehicle to run a simulation. The physical model of a vehicle was constructed with CarSim, a simulation-package software developed by Mechanical Simulation Corporation of the United States. The algorithms were developed for each function such as ACD and AYC, not for each vehicle type. Therefore, the algorithms can be employed by various types of vehicles.
Concept components for 2010 Outlander
The 2010MY Outlander adopts a new S-AWC (Super All Wheel Control) that has added and refined an active front differential that controls the differential limiting force of the left and right front wheels based on an electronically controlled 4WD that distributes drive force to the rear wheels and integrates this Active Stability Control (ASC) and ABS. The result is greater turning performance, stability and drive performance while maintaining fuel economy equal to traditional electronically-controlled 4WD.
Structure
The S-AWC ECU calculates the amount of control according to drive condition and vehicle behavior based on sensor and switch data and ECU operation data. Control instructions are sent to the active front diff and electronic control couplings.
Active control differential
Electronically-controlled couplings used in electronic –control 4WD are located in the transfer case to limit differential between the front left and right wheels and control drive force distribution on either side.
Electronic control coupling
An electronic control coupling within the rear differential distributes drive force to the rear wheels according to driving conditions. This is the same as used for 4WD electronic control in the 2009 model Outlander
S-AWC ECU
The optimal amount of drive force control is calculated from sensor information obtained from CAN communications etc. to control the active front diff and the electronically-controlled coupling. Compared with the 2009 Outlander, Microcomputer performance has been enhanced and calculation speed and accuracy have been improved.
Sensor information
Compared with electronically-controlled 4WD, sensor information has been significantly augmented to accurately assess vehicle driving conditions and realize highly-responsive, finely tuned control.
S-AWC control mode switch
S-AWC in the 2010 model Outlander has three selectable modes of control (NORMAL/SNOW/OFFROAD) that have been tuned to suit the road surface. Making the switch according to road surface conditions enables proper control.
Indicator
S-AWC control information will be constantly displayed on the upper level of the multi-information display. A dedicated screen has been provided to display S-AWC operation information. The center displays traction control condition while yaw movement control conditions are displayed on either side.
Control
Changes to the 2009 Outlander’s electronically-controlled 4WD.
1) Addition of integrated control with the active front differential
In addition to front and rear drive force distribution, enabling integrated control of drive force distribution to both front wheels delivers a higher level of driving on all fronts (turning performance, stability and road performance) compared with the 2009 Outlander:
2) Introduction of a yaw rate feedback control
Vehicle behavior faithful to drive input is realized by precise assessment of vehicle turning movement based on yaw rate sensor data and the provision of achieve close to target vehicle behavior obtained from speed and steering angle.
3) Evolution of coordinated ASC/ABS control
Properly controlling active front differential and electronically controlled coupling according to the operating status of ASC and ABS, improves turning performance and stability.
Concept components for 2014 Outlander
Following function newly added.
Brake control
When the under steer condition, the beginning of turning response by steering operation is dramatically improved by adding the brake force to the inner wheel.
In addition, the wheel slippage is reduced during start moving.
EPS control
Suppress the steering wheel movement which generated by the slippery road.
As a result, the traction performance improves because the amount of the control of Active Front Differential (AFD) can be increased.
Synchronized with ECO MODE
By selecting the ECO MODE, Engine and climate control are controlled as a “ECO mode”. Likewise, S-AWC control also turn to AWC ECO.
At the result of these control, Eco driving condition is easy to prepare for the driver.
Control
S-AWC Control Mode
By pushing S-AWC Control switch, the control mode can be changed.
Concept components for Outlander PHEV
Fail-safe function
Fault detection
The ECU performs the following checks at the appropriate moment. The ECU determines that a fault has occurred when the fault detection conditions are met. Then the ECU stores the diagnosis code and ensures that the vehicle can still be driven. When the failure resume conditions are met, ECU determines the status is normal, and resumes the system. Start-up (Initial check immediately after the power supply mode of the electric motor switch is turned on.)
• CPU check
• Performs the ROM and RAM checks.
Always (while the power supply mode of the electric motor switch is turned on except during initial check)
1. CPU check
• Performs CAN communication and interactive check between CPUs.
2. Power supply check
• Monitors the CPU supply voltage and checks if the voltage is within specifications.
3. External wire connection check
• Checks if the input and output of each external wire connection is open or shorted.
4WD lock switch
The 4WD lock switch is located on the floor console. When the 4WD lock switch is pressed with the electric motor switch ON, "4WD LOCK" will be turned on and off. When the 4WD lock switch is turned on with the drive mode at ECO, or the ECO mode switch is turned on with the drive mode at 4WD lock, the drive mode will be switched to "ECO MODE/4WD LOCK". The driver can obtain better ground-covering ability by choosing the drive mode between "4WD LOCK" and "ECO MODE/4WD LOCK". When the ECO mode switch is turned off, the drive mode will return from "ECO MODE/4WD LOCK" to "4WD LOCK".
Cornering Performance
Enhancement of the cornering stability
It is optimization of the torque distribution ratio between front and rear wheels when cornering. In order to keep the cornering stability against the direction of steering wheel on the slippery road.
Enhancement of the vehicle maneuverability
The optimization of the control value for the AYC (Active Yaw Control) with braking, in order to enhance the vehicle maneuverability.
Traction performance
Launching performance on the icy slope is enhanced.
Идея сделать чип-тюнинг своего Mitsubishi Outlander 3 возникла после очередной опасной ситуации на дороге.
Я вынужденно припарковался на прямом участке трассы в темное время суток, что бы переслать информацию. На трассе две полосы и широкая асфальтированная обочина, вдоль всей трассы, на которой я и встал «на аварийке».
Закончив отправку, посмотрел в зеркало, место для выезда было, включил драйв, начал движение по обочине, где то на 60 выехал на трассу, нажал газ и . 80 . дальше гул движка и недовольная фура мигает мне светом. В общем я разгонялся медленнее чем тормозил груженый лесом грузовик и чудом не случилось ДТП.
Аут рычал и не ехал, с трудом разогнался помигал «аварийкой» и решил ехать к дилеру прошивать мотор.
Машина 2013 года с двигателем 2.4, обслуживается каждые 10т масло Motul или Idemitsu.
На следующий день записался в Максимум на «чип-тюнинг».
Изначально я был скептически настроен относительно «обновления ПО» двигателя. Отзывов по своему двигателю как таковых я не нашел, читал только, что 2х литровая версия «чипуется» лучше, прирост мощности больше. Это мне подтвердил мастер, когда приехал в автосервис.
Прошивка занимает час и стоит 15000р. В интернете множество сайтов где стоимость ниже, но рисковать машиной не хочется.
Дилер «Максимум» на Руставели гарантирует качество и есть возможность полного отката с возвратом средств, если результат не устраивает.
«Прошивали» мой outlander на самом деле 10 минут, дольше мыли кузов, такие правила у дилера. Моют надо заметить авто отлично.
Забрал машину как и обещали через час, поблагодарил мастера и отправился домой.
Выехал и сразу встал в пробку в сторону КАД, но «толкаться» в пробке аут стал по другому. Исчез привычный рев и провал на старте, машина сразу едет и бодро едет. Не как BMW, но не тупит и резво ныряет носом туда, куда направляешь.
Когда выехал на КАД сразу нажал газ, аут начал быстро и равномерно разгоняться. Пропал привычный рев и пропадание мощности от 2,5 до 4 тыс. сразу стрелка уходит в 5 тыс и начинается разгон, 120 км/ч набирает быстро. Нет потери мощности и на обгоне, машина сразу разгоняется.
После двух дней езды, могу сказать что ощущения от машины радуют. Аутлендер стал намного динамичнее, более предсказуемый это удобно.
OUT III: Делаем S-AWC на Outlander: репрограмминг блока AWC. Блок S-AWC от Mitsubishi Eclipse Cross на Mitsubishi Outlander
Блок S-AWC от Eclipse Cross на Outlander
Продолжаем доработку Аута, а именно хотел поделиться своими наблюдениями об установленном блоке
S-AWC (Super All Wheell Control), как на Eclipse Cross. В целом показалось что руль стал более острей, двигатель не тупит при проезде «лежачих полицейских». Экстремально в повороты входить не пробовал пока, но говорят теперь можно! Да в режиме AUTO теперь машина едет увереннее. теперь это режим SNOW
Так, что «новомодная коробка S-AWC» пока радует. Наблюдать за ее работай буду и дальше!
Новая кнопка переключения режимов полного привода
А, вот и сама коробка S-AWC
Информация для общего развития
Режимы теперь называются иначе
Учу поиску. Дорого. С гарантией! ==>>> Подробнее тут
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Eclipse Cross==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi ASX, Peugeot 4008, Citroen C4 Aircross==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander XL, Peugeot 4007, Citroen C-Crosser==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander III (2013-2015MY)==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander IV (2015-2019MY)==>>>
Учу поиску. Дорого. С гарантией! ==>>> Подробнее тут
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Eclipse Cross==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi ASX, Peugeot 4008, Citroen C4 Aircross==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander XL, Peugeot 4007, Citroen C-Crosser==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander III (2013-2015MY)==>>>
- Путеводитель Mitsubishi Outlander IV (2015-2019MY)==>>>
Система Mitsubishi S-AWC: от концепта в реальность. Немного о эволюции системы
S-AWC (Super All Wheel Control) is the brand name of an advanced full-time four-wheel drive system developed by Mitsubishi Motors. The technology, specifically developed for the new 2007 Lancer Evolution, the 2010 Outlander (if equipped), the 2014 Outlander (if equipped), the Outlander PHEV and the Eclipse Cross have an advanced version of Mitsubishi Motors' AWC system. Mitsubishi Motors first exhibited S-AWC integration control technology in the Concept-X model at the 39th Tokyo Motor Show in 2005.[4] According to Mitsubishi Motors, "the ultimate embodiment of the company's AWC philosophy is the S-AWC system, a 4WD-based integrated vehicle dynamics control system".
It integrates management of its Active Center Differential (ACD), Active Yaw Control (AYC), Active Stability Control (ASC), and Sports ABS components, while adding braking force control to Mitsubishi Motors' own AYC system, allowing regulation of torque and braking force at each wheel. S-AWC employs yaw rate feedback control, a direct yaw moment control technology that affects left-right torque vectoring (this technology forms the core of S-AWC system) and controls cornering maneuvers as desired during acceleration, steady state driving, and deceleration. Mitsubishi Motors claims the result is elevated drive power, cornering performance, and vehicle stability regardless of driving conditions.
Components
Active Center Differential (ACD)
Active Center Differential incorporates an electronically-controlled hydraulic multi-plate clutch. The system optimizes clutch cover clamp load for different driving conditions, regulating the differential limiting action between free and locked states to optimize front/rear wheel torque split and thereby producing the best balance between traction and steering response.
Active Yaw Control (AYC)
Active Yaw Control uses a torque transfer mechanism in the rear differential to control rear wheel torque differential for different driving conditions and so limit the yaw moment that acts on the vehicle body and enhance cornering performance. AYC also acts like a limited slip differential by suppressing rear wheel slip to improve traction. In its latest form, AYC now features yaw rate feedback control using a yaw rate sensor and also gains braking force control. Accurately determining the cornering dynamics on a realtime basis, the system operates to control vehicle behavior through corners and realize vehicle behavior that more closely mirrors driver intent.
Active Stability Control (ASC)
Active Stability Control stabilizes vehicle attitude while maintaining optimum traction by regulating engine power and the braking force at each wheel. Taking a step beyond the previous generation Lancer Evolution, the fitting of a brake pressure sensor at each wheel allows more precise and positive control of braking force. ASC improves traction under acceleration by preventing the driving wheels from spinning on slippery surfaces. It also elevates vehicle stability by suppressing skidding in an emergency evasive maneuver or the result of other sudden steering inputs.
Sport ABS
The Sports ABS system supports braking when entering into a corner by controlling power to all tyres depending on handling characteristics. Braking can be controlled to obtain optimal damping at each tyre based on information from four wheel-speed sensors and steering wheel angle sensor. The addition of yaw rate sensors and brake pressure sensors to the Sport ABS system has improved braking performance through corners compared to the Lancer Evolution IX.
Concept components for 2007 Lancer Evolution
The prototype system also featured two additional components controlling suspensions and steering, which failed to make the production version of S-AWC system:
- Active Steering System
- Roll Control Suspension (RCS)
Active Steering System realizes handling with more linear response by adaptively controlling front wheel turn angle according to steering input and vehicle speed. At slower vehicle speeds the system improves response by shifting to a quicker steering gear ratio, while at higher speeds it substantially improves stability by moving to a slower gear ratio. For rapid steering inputs, S-AWC momentarily increases front wheel turn angle and Super AYC control to realize sharper response. In countersteer situations, S-AWC increases responsiveness further to assist the driver with steering precision.
RCS effectively reduces body roll and pitching by hydraulically connecting all the shock absorbers together and regulating their damping pressures as necessary. Able to control both roll and pitching stiffness separately, RCS can operate in a variety of ways. It can, for example, reduce roll only when required during turn in or in other situations while being set up on the soft side to prioritize tire contact and ride comfort. Since the system controls roll stiffness hydraulically, it eliminates the need for stabilizer bars. In the integrated control of its component systems, S-AWC employs information from RCS's hydraulic system to estimate the tire load at each wheel.
Control system
The use of engine torque and brake pressure information in the regulation of the ACD and AYC components allows the S-AWC system to determine more quickly whether the vehicle is accelerating or decelerating. S-AWC also employs yaw rate feedback for the first time. The system helps the driver follow his chosen line more closely by comparing how the car is running, as determined from data from the yaw rate sensors, and how the driver wants it to behave, as determined from steering inputs, and operates accordingly to correct any divergence. The addition of braking force regulation to AYC's main role of transferring torque between the right and left wheels allows S-AWC to exert more control over vehicle behavior in on-the-limit driving situations. Increasing braking force on the inside wheel during understeer and on the outer wheel during oversteer situations, AYC's new braking force control feature works in conjunction with torque transfer regulation to realize higher levels of cornering performance and vehicle stability.
- Tarmac for dry, paved surfaces;
- Gravel for wet or unmade surfaces;
- Snow for snow-covered surfaces.
ECU integration
Two electronic control units (ECU) regulate vehicle motion. One is an ECU developed by Mitsubishi Electric to control ACD and AYC. The other is an ECU developed by Continental Automotive Systems of Germany that controls ASC and ABS. The two ECUs can communicate with other ECUs through a CAN, an in-vehicle LAN interface standard. In addition, the two ECUs are communicating with each other through a dedicated CAN, enabling vehicle motion to be controlled more quickly. The cable and communication standard for the dedicated CAN are the same as those for other CANs.
A longitudinal acceleration sensor, lateral acceleration sensor and yaw rate sensor are installed as one module near the gravity center of a vehicle, which is located between the driver's and passenger's seats. Other sensors, such as a wheel-speed sensor and steering-angle sensor, are installed in different places. However, no vertical acceleration sensor is used.
Also, when the vehicle is equipped with Mitsubishi's Twin Clutch SST transmission, S-AWC analyzes the behavior of the turning vehicle and if it judges that it is safer not to shift gears, it sends a signal to tell Twin Clutch SST that the gear must not be changed. However, S-AWC does not control vehicle motion by using control information from Twin Clutch SST. The co-operation is a one-way communication.
The control algorithms of vehicle motion were developed by Mitsubishi in-house, with MATLAB and Simulink: control system modeling tools. Mitsubishi adopted model-based method, which combines an algorithm and physical model of a vehicle to run a simulation. The physical model of a vehicle was constructed with CarSim, a simulation-package software developed by Mechanical Simulation Corporation of the United States. The algorithms were developed for each function such as ACD and AYC, not for each vehicle type. Therefore, the algorithms can be employed by various types of vehicles.
Concept components for 2010 Outlander
The 2010MY Outlander adopts a new S-AWC (Super All Wheel Control) that has added and refined an active front differential that controls the differential limiting force of the left and right front wheels based on an electronically controlled 4WD that distributes drive force to the rear wheels and integrates this Active Stability Control (ASC) and ABS. The result is greater turning performance, stability and drive performance while maintaining fuel economy equal to traditional electronically-controlled 4WD.
Structure
The S-AWC ECU calculates the amount of control according to drive condition and vehicle behavior based on sensor and switch data and ECU operation data. Control instructions are sent to the active front diff and electronic control couplings.
Active control differential
Electronically-controlled couplings used in electronic –control 4WD are located in the transfer case to limit differential between the front left and right wheels and control drive force distribution on either side.
Electronic control coupling
An electronic control coupling within the rear differential distributes drive force to the rear wheels according to driving conditions. This is the same as used for 4WD electronic control in the 2009 model Outlander
S-AWC ECU
The optimal amount of drive force control is calculated from sensor information obtained from CAN communications etc. to control the active front diff and the electronically-controlled coupling. Compared with the 2009 Outlander, Microcomputer performance has been enhanced and calculation speed and accuracy have been improved.
Sensor information
Compared with electronically-controlled 4WD, sensor information has been significantly augmented to accurately assess vehicle driving conditions and realize highly-responsive, finely tuned control.
S-AWC control mode switch
S-AWC in the 2010 model Outlander has three selectable modes of control (NORMAL/SNOW/OFFROAD) that have been tuned to suit the road surface. Making the switch according to road surface conditions enables proper control.
Indicator
S-AWC control information will be constantly displayed on the upper level of the multi-information display. A dedicated screen has been provided to display S-AWC operation information. The center displays traction control condition while yaw movement control conditions are displayed on either side.
Control
Changes to the 2009 Outlander’s electronically-controlled 4WD.
1) Addition of integrated control with the active front differential
In addition to front and rear drive force distribution, enabling integrated control of drive force distribution to both front wheels delivers a higher level of driving on all fronts (turning performance, stability and road performance) compared with the 2009 Outlander:
2) Introduction of a yaw rate feedback control
Vehicle behavior faithful to drive input is realized by precise assessment of vehicle turning movement based on yaw rate sensor data and the provision of achieve close to target vehicle behavior obtained from speed and steering angle.
3) Evolution of coordinated ASC/ABS control
Properly controlling active front differential and electronically controlled coupling according to the operating status of ASC and ABS, improves turning performance and stability.
Concept components for 2014 Outlander
Following function newly added.
Brake control
When the under steer condition, the beginning of turning response by steering operation is dramatically improved by adding the brake force to the inner wheel.
In addition, the wheel slippage is reduced during start moving.
EPS control
Suppress the steering wheel movement which generated by the slippery road.
As a result, the traction performance improves because the amount of the control of Active Front Differential (AFD) can be increased.
Synchronized with ECO MODE
By selecting the ECO MODE, Engine and climate control are controlled as a “ECO mode”. Likewise, S-AWC control also turn to AWC ECO.
At the result of these control, Eco driving condition is easy to prepare for the driver.
Control
S-AWC Control Mode
By pushing S-AWC Control switch, the control mode can be changed.
Concept components for Outlander PHEV
Fail-safe function
Fault detection
The ECU performs the following checks at the appropriate moment. The ECU determines that a fault has occurred when the fault detection conditions are met. Then the ECU stores the diagnosis code and ensures that the vehicle can still be driven. When the failure resume conditions are met, ECU determines the status is normal, and resumes the system. Start-up (Initial check immediately after the power supply mode of the electric motor switch is turned on.)
• CPU check
• Performs the ROM and RAM checks.
Always (while the power supply mode of the electric motor switch is turned on except during initial check)
1. CPU check
• Performs CAN communication and interactive check between CPUs.
2. Power supply check
• Monitors the CPU supply voltage and checks if the voltage is within specifications.
3. External wire connection check
• Checks if the input and output of each external wire connection is open or shorted.
4WD lock switch
The 4WD lock switch is located on the floor console. When the 4WD lock switch is pressed with the electric motor switch ON, "4WD LOCK" will be turned on and off. When the 4WD lock switch is turned on with the drive mode at ECO, or the ECO mode switch is turned on with the drive mode at 4WD lock, the drive mode will be switched to "ECO MODE/4WD LOCK". The driver can obtain better ground-covering ability by choosing the drive mode between "4WD LOCK" and "ECO MODE/4WD LOCK". When the ECO mode switch is turned off, the drive mode will return from "ECO MODE/4WD LOCK" to "4WD LOCK".
Cornering Performance
Enhancement of the cornering stability
It is optimization of the torque distribution ratio between front and rear wheels when cornering. In order to keep the cornering stability against the direction of steering wheel on the slippery road.
Enhancement of the vehicle maneuverability
The optimization of the control value for the AYC (Active Yaw Control) with braking, in order to enhance the vehicle maneuverability.
Traction performance
Launching performance on the icy slope is enhanced.
Читайте также:

